ZYS provides high quality bearing products and professional bearing solutions for users in the fields of machine tool, wind power, metallurgy, automobile and rail transportation, construction machinery, etc. ZYS can perform batch production of various bearing products with inner diameter of 0.6mm to outer diameter of 6.8m. In addition to bearings, ZYS can also offer high-speed spindles, precision bearing instruments, bearing testing machines, bearing manufacturing machines and bearing parts.
ZYS precision angular contact ball bearings consist of high-precision angular contact bearings (standard series),super high-speed angular contact ball bearings,high-speed sealed angular contact ball bearings and high-speed spindle bearings.
In the metallurgical industry, the working environment of rolling mills, continuous casting machine or converters is really harsh. These conditions require bearings to withstand the harsh effects of heavy load, high temperature, dust and water. In order to meet the requirements of metallurgical industry, ZYS R & D teamhas developed bearings products with high quality, high precision and long service life and also can offer the bearing solutions for manufacturers in the metallurgical industry.
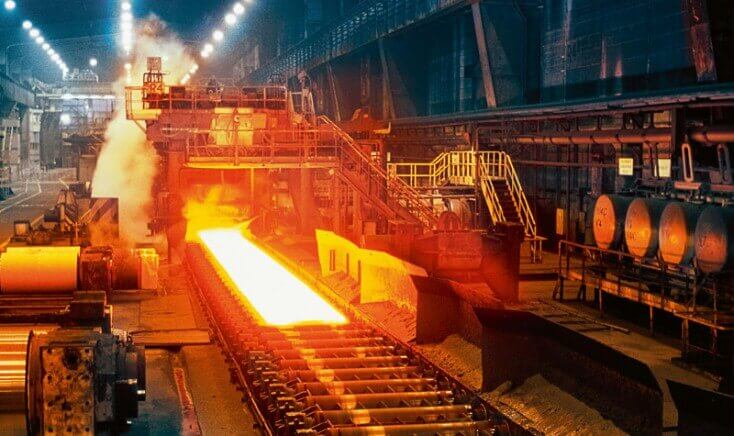

ZYS large-size heavy duty precision bearings are manufactured in our second industry park,which covers 133,333㎡ with total investment of 438 million RMB.
The inner ring,outer ring and rolling elements of bearing under normal working conditions are made of high carbon chromium bearing steel.To meet the special requirements,such as super high speed,wear-resisting,low temperature rising,long life and high reliability etc.,it’s suggested to use hybrid ceramic ball bearings.

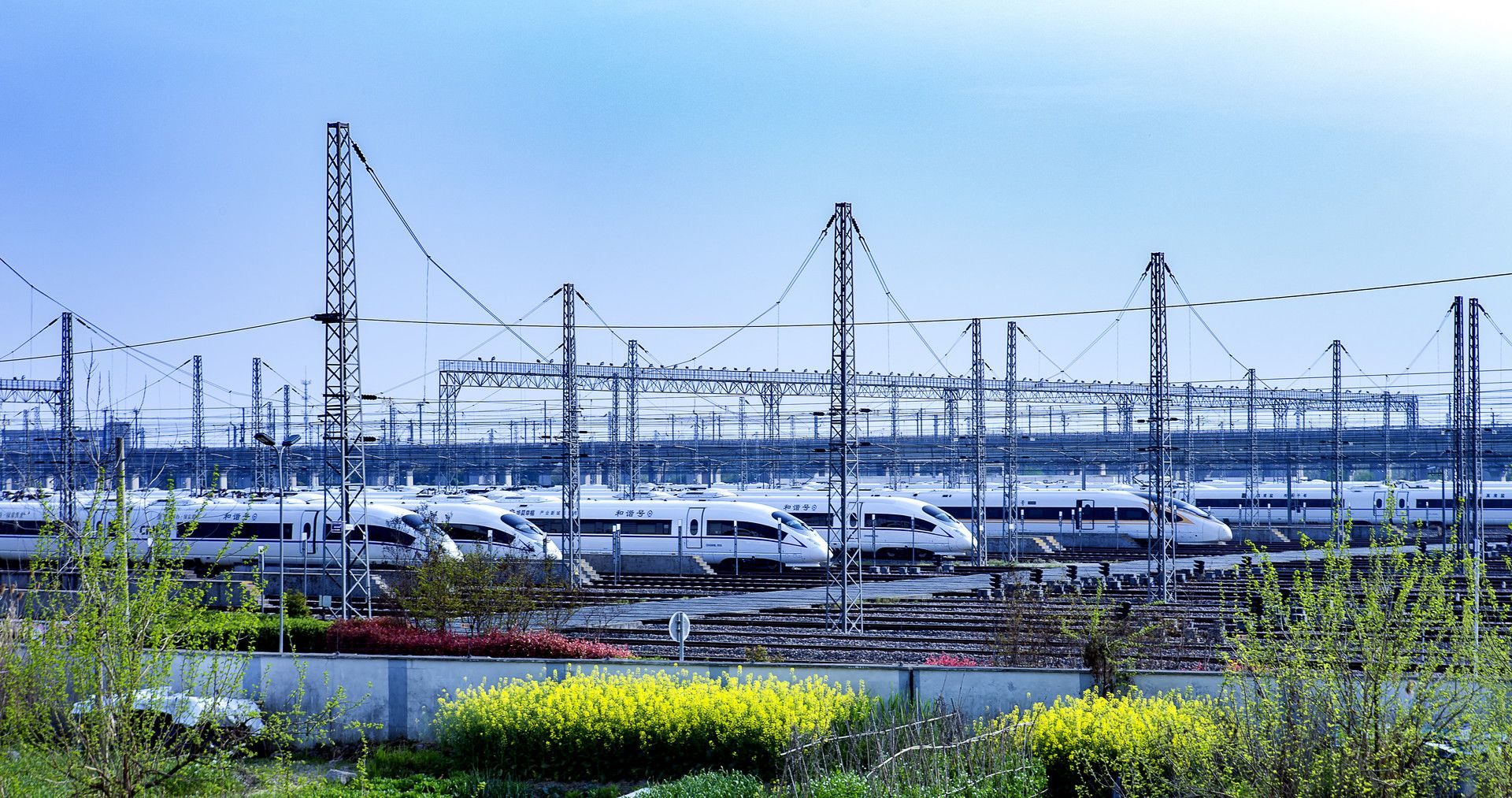
ZYS has been committed to the research and development of bearings for rail transportation for a long time to meet the increasing requirements for rail transportation,such as higher speed,load,reliability and etc.

ZYS plays an leading role in aerospace bearing industry of China,We has successfully accomplished the bearing assemblies for “Dong fang hong” series man-made satellite,manned spacecraft series from “Shenzhou Ⅰ” to “Shenzhou Ⅹ”,“Chang’E” lunar exploration program,successful docking from “Shenzhou Ⅷ” and “Shenzhou Ⅸ” to Tiangong target aircraft.

ZYS automobile bearings include tapered roller bearings,cylindrical roller bearings,deep groove ball bearings and angular contact ball bearings,among which clutch bearings and the hub bearings units of the first,second and third generation are mainly used to gear box,axles,transmission system and other parts of all kinds of automobiles.We have conducted thorough research on wheel hub bearings,clutch release bearing,constant velocity cardan joint,gear box bearings and etc

ZYS can supply batch production of various bearing manufacturing equipments,like CNC cutting equipments and automatic production line for bearing rings,automatic grinder,superfinishing machine,precision cold rolling machine for bearing rings,semi-automatic multi-purpose grinder for miniature ball bearing rings and other precision manufacturing equipments for bearing.

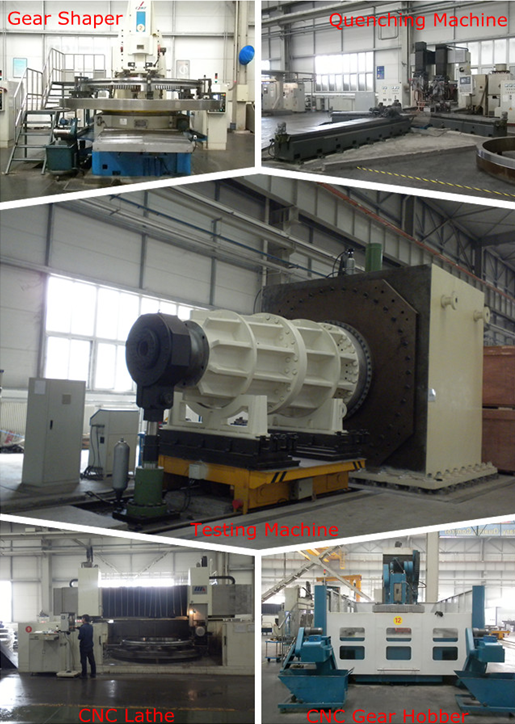
Besides all kinds of bearing products,bearing measuring machines are also our main products,which have been exported to India,Iran,Romania,Brazil and many other countries.Our main measuring machines include the instruments for measuring the dimension accuracy,roundness,profile and roughness of bearing parts,the instruments for inspecting bearing performance and other instruments used to automatically inspect and control various parameters during manufacturing process.These instruments are widely used in bearing workshops,inspection stations,measuring room and assembly factories.

ZYS has conducted in-depth research on bearing testing technology and reliability theory of all kinds of bearings,engaging in the development and manufacture of bearing testing equipments and undertaking the simulation testing,life testing and other performance tests for all kinds of bearings.We can also develop and manufacture the simulation testing machines in full-automatic control for the bearings used in various machineries (aviation,spaceflight,railway,automobile,motorcycle,machine tool,motor,etc.)

Since 1958, ZYS has been committed to the research and development of “high-tech, precise, cutting-edge, specialized and special” bearings, and relevant products. Our products have been used for mining, metallurgy, wind turbine generator, machine tool, machinery, medical treatment, automobile, rail transport, etc.

Wind turbine bearings are core components of wind power generation systems, operating in extreme environments with high maintenance costs, and requiring exceptional durability and reliability. As wind power is a vital renewable energy source, its development heavily depends on the support of high-performance bearings. The main bearings in wind turbines include yaw bearing assemblies, main shaft bearings, gearbox bearings, and generator bearings, with structural types covering four-point contact ball bearings, crossed roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, spherical roller bearings, and deep groove ball bearings. Among these, large yaw bearings and main shaft bearings present significant technical challenges, relying heavily on imports for a long time. These are critical bottlenecks for the localization of wind turbines. Achieving localization of wind turbine bearings will not only enhance the design and application level of the domestic bearing industry, narrow the gap with international standards, and promote technological progress in the industry, but also effectively reduce wind power costs and accelerate the development of China's renewable energy sector.Wind turbines operate year-round in harsh outdoor environments, enduring significant variations in temperature, humidity, and load, with wind speed peaks reaching up to 23 m/s and impact loads present. Therefore, wind turbine bearings must feature excellent sealing and lubrication performance, impact resistance, longevity, and high reliability. Wind turbines need to start and track wind direction changes at low wind speeds , requiring bearing structures to be specially designed for low friction and high sensitivity. Large yaw bearings often require gear teeth on the outer ring. To ensure optimal turbine operation, the design, material selection, manufacturing process, lubrication solutions, and sealing technology of bearings all need targeted research and development to significantly improve equipment performance and reliability. Since turbines are often installed in hard-to-access areas such as mountains, deserts, and coastlines, system maintenance is critical. Condition monitoring systems can effectively track the performance of the drivetrain, while predictive maintenance enhances system reliability and efficiency, increasing effective operating time. Technologies such as vibration analysis, oil analysis, and infrared thermography can accurately determine the optimal maintenance timing. Predictive maintenance strategies significantly enhance operational reliability by implementing repairs only when necessary, avoiding over-maintenance, and reducing costs.We provide high-performance wind turbine bearings tailored to meet the demanding requirements of the industry. With advanced design, manufacturing, and maintenance solutions, we are committed to supporting the development of renewable energy and ensuring the reliable operation of wind power systems.
2026-03-02 14:36:15 move
Key Components of Wind Turbine Bearings and Their Critical Role in Renewable Energy Development
2026-03-02 14:36:15Wind turbine bearings are core components of wind power generation systems, operating in extreme environments with high maintenance costs, and requiring exceptional durability and reliability. As wind power is a vital renewable energy source, its development heavily depends on the support of high-performance bearings. The main bearings in wind turbines include yaw bearing assemblies, main shaft bearings, gearbox bearings, and generator bearings, with structural types covering four-point contact ball bearings, crossed roller bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, spherical roller bearings, and deep groove ball bearings. Among these, large yaw bearings and main shaft bearings present significant technical challenges, relying heavily on imports for a long time. These are critical bottlenecks for the localization of wind turbines. Achieving localization of wind turbine bearings will not only enhance the design and application level of the domestic bearing industry, narrow the gap with international standards, and promote technological progress in the industry, but also effectively reduce wind power costs and accelerate the development of China's renewable energy sector.Wind turbines operate year-round in harsh outdoor environments, enduring significant variations in temperature, humidity, and load, with wind speed peaks reaching up to 23 m/s and impact loads present. Therefore, wind turbine bearings must feature excellent sealing and lubrication performance, impact resistance, longevity, and high reliability. Wind turbines need to start and track wind direction changes at low wind speeds , requiring bearing structures to be specially designed for low friction and high sensitivity. Large yaw bearings often require gear teeth on the outer ring. To ensure optimal turbine operation, the design, material selection, manufacturing process, lubrication solutions, and sealing technology of bearings all need targeted research and development to significantly improve equipment performance and reliability. Since turbines are often installed in hard-to-access areas such as mountains, deserts, and coastlines, system maintenance is critical. Condition monitoring systems can effectively track the performance of the drivetrain, while predictive maintenance enhances system reliability and efficiency, increasing effective operating time. Technologies such as vibration analysis, oil analysis, and infrared thermography can accurately determine the optimal maintenance timing. Predictive maintenance strategies significantly enhance operational reliability by implementing repairs only when necessary, avoiding over-maintenance, and reducing costs.We provide high-performance wind turbine bearings tailored to meet the demanding requirements of the industry. With advanced design, manufacturing, and maintenance solutions, we are committed to supporting the development of renewable energy and ensuring the reliable operation of wind power systems.
move
The Application of Four Point Angular Contact Ball Bearings in Wind Turbines
2026-02-02 16:42:27In the growing field of renewable energy, wind turbines have become one of the most important solutions for reducing carbon emissions and ensuring a sustainable future. Behind the scenes, the reliability and efficiency of these large structures depend heavily on the engineering precision of their components. One critical component is the four point angular contact ball bearing, which plays a vital role in the rotating mechanisms of wind turbines. What is a Four Point Angular Contact Ball Bearing? A four point contact ball bearing is a type of single-row bearing that can handle axial loads in both directions as well as limited radial loads. It differs from traditional angular contact bearings because the raceways are designed so that the ball contacts the inner and outer rings at four distinct points. This unique contact geometry allows one bearing to handle what would normally require a pair of angular contact bearings. These bearings are especially suitable for applications where space and weight are limited but high performance is still needed—making them an excellent choice for wind turbines. Role in Wind Turbines In wind turbines, four point angular contact ball bearings are mainly used in yaw systems and blade pitch systems. These areas require bearings that can support combined axial and radial loads while offering rigidity and low friction for efficient rotation. Yaw System: The yaw mechanism turns the nacelle to face the wind. Bearings here must manage high axial loads due to wind pressure and must do so with precision to ensure alignment. Blade Pitch System: The pitch system rotates turbine blades to control rotor speed, especially during changing wind conditions. This requires quick, responsive, and durable bearing action. Key Advantages in Wind Applications Using four point angular contact ball bearings in wind turbines brings a range of benefits: Compact Design: One bearing manages axial loads in both directions, reducing space and weight requirements. High Load-Carrying Capacity: Ideal for heavy axial and moderate radial loads found in wind turbine operation. Improved System Reliability: Reduces the need for multiple bearings, improving alignment and reducing wear. Low Maintenance: Designed to last for years with minimal lubrication needs and extended service intervals. Material and Durability Considerations Bearings used in wind turbines must resist harsh environmental conditions such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, and contamination. High-grade bearing steel, advanced heat treatment, and effective sealing technologies are often used in the production of four point contact ball bearings for wind applications. Additionally, to improve service life and operational stability, manufacturers implement raceway precision grinding and optimized internal geometry to reduce stress concentration and increase fatigue resistance. Conclusion The application of four point angular contact ball bearings in wind turbines is not only about fulfilling mechanical demands—they are essential for enhancing the turbine's efficiency and dependability. As wind energy continues to expand globally, so does the importance of selecting the right bearing solution for complex wind turbine systems. For OEMs and maintenance professionals, understanding the advantages and specifications of four point angular contact ball bearings can significantly impact turbine performance and lifetime. As always, consulting with bearing manufacturer ZYS and our engineers can guide optimal bearing selection for specific turbine designs and site requirements.
move
Applications and Advantages of Four Point Angular Contact Ball Bearings | Precision Bearings
2026-01-26 15:51:46In the world of precision engineering and industrial machinery, Four Point Angular Contact Ball Bearings play a crucial role in handling combined loads and optimizing design space. These specialized bearings are widely used across industries such as robotics, machine tools, and automotive systems due to their unique structure and performance characteristics.What Are Four Point Angular Contact Ball Bearings?A Four Point Angular Contact Ball Bearing is a type of single-row bearing designed to support axial loads in both directions, as well as limited radial loads. The inner ring is split into two halves, enabling the bearing to form four contact points with the balls — hence the name. This design allows the bearing to accommodate complex loading conditions with high precision.Key ApplicationsIndustrial Machinery:In heavy-duty equipment like CNC machines and gearboxes, four point bearings are used to support rotating shafts that experience both axial and radial loads. Their compact design allows for space-saving integration while maintaining high load capacity.Robotics and Automation:In robotic arms and automated systems, precision and responsiveness are critical. These bearings help reduce friction and support multi-directional loads, enabling smoother and more accurate movements.Wind Turbines:The bearings are also used in yaw and pitch systems of wind turbines where they handle high axial loads and oscillating movements.Medical Equipment:High-precision devices like CT scanners and surgical robots rely on compact and accurate bearing systems. Four point angular contact bearings provide the needed performance without increasing the size of the device.Advantages of Four Point Angular Contact Ball BearingsSpace Efficiency:They combine the function of two single-row angular contact bearings, reducing the number of components and saving space.Cost-Effective Design:Fewer parts mean simpler assembly and lower overall system cost.High Axial Load Capacity:Capable of supporting axial loads in both directions, making them ideal for applications where load direction can vary.Precision and Durability:Manufactured to tight tolerances, these bearings ensure high accuracy and long service life, even under demanding conditions.Selection ConsiderationsWhen choosing a four point angular contact ball bearing, it's essential to consider factors such as:Load direction and magnitudeOperating speedInstallation spaceLubrication and maintenance requirementsConclusionFour Point Angular Contact Ball Bearings are an integral component in modern mechanical systems, offering a reliable and efficient solution for complex loading conditions. Whether you're designing high-speed machinery, compact assemblies, or precision instruments, understanding the capabilities of these bearings can help you make better engineering decisions.For more information or to find the right bearing for your application, feel free to contact our technical team.
move